
Third, the potential environmental impact of this technology is still unclear. Second, the materials’ reliability and lifespan are still questionable. First, the cost of equipment and materials are hurdles to be overcome to allow mass production. The two areas where 4D bioprinting is mostly used in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering for fabricating complex tissue/organ geometries and controlling the tissue microarchitecture with 3D printing. In recent years, though, researchers have developed ways to make this innovative technology even more sophisticated by tapping into the fourth dimension. Like every other technology far from the maturity stage, many aspects must be figured out. The 3D printing process is used across a range of industrial sectors, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and even food and beverage. If a single item is to be used for multiple purposes, this could reduce the need for disposable products. Given the increase in manufacturing efficiency, 4D printing could result in a potential reduction of waste. These could really transform manufacturing – and thus our daily life’s objects – in such a way that we can’t even imagine yet. Potentially, 4D printing could make it possible to set up infrastructure that can change depending on the weather – think of a bridge that could expand during a flood.Īnother advantage lies in the usage of new smart materials. This leads to the possibility of creating structures that would be impossible to build with current manufacturing techniques. Through computational folding, bigger items can be reproduced as only one part. Three dimensions (3D) are characterized by the presence (expansion) of the target item in the x, y, and z planes. On the other hand, four dimensions are tough to feel and notice. However, in 4D printing, the resulting 3D shape is able to morph into different forms in response to environmental stimulus, with the 4th dimension being the time-dependent shape change after the printing. New research published to Materials Horizons by a team from Rutgers University.
#3d vs 4d printing pro#
What are the main advantages?ĤD printing’s main pro is the possibility to print objects larger than the used printer. Inspired by the principle of self-assembly, 4D printing is the process by which a 3D printed object is transformed into a different structure by the influence. The main difference between three and four dimensions is that three dimensions are quickly sensed. 3D printing has promised a revolution in manufacturing, but 4D printing could usher in something truly extraordinary. This means that, depending on their application, they may be able to elongate, fold, and bend when activated.
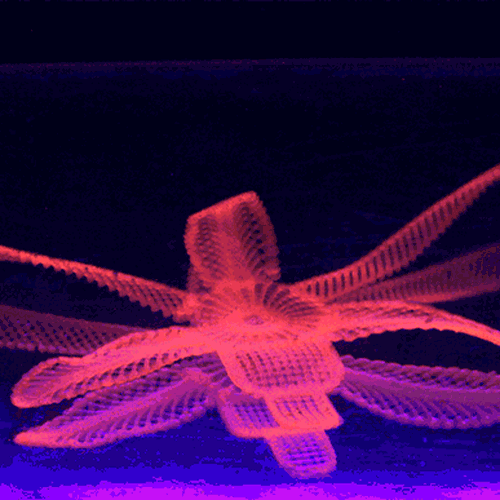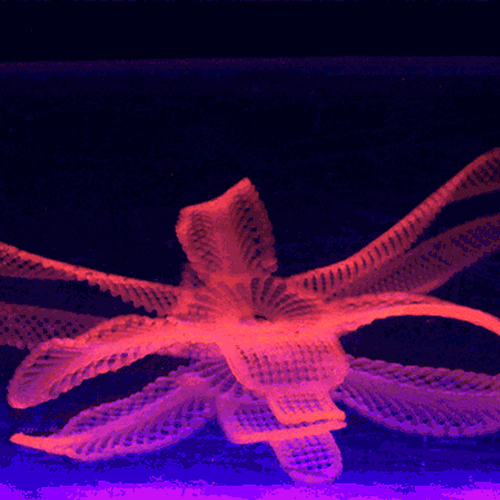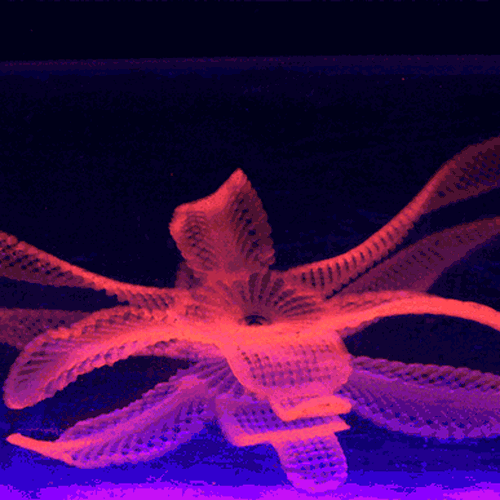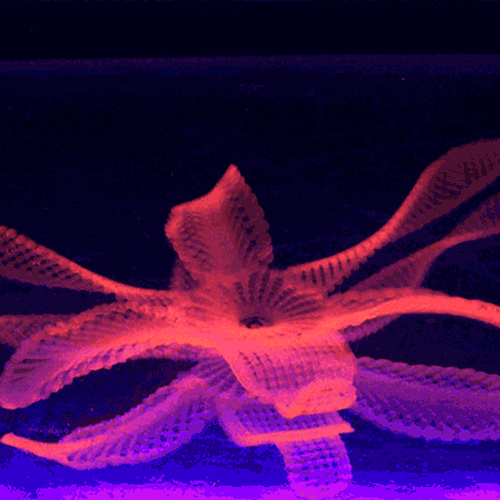
By contrast, 3D-printed objects have rigidity as one of their features, meaning that they will keep the same shape once fabricated.įour-dimensional printed items react to heat, water, or electricity – to name a few catalysts – based on the instructions written on their geometrical coding. These are hydrogels or memory polymers that – thanks to their properties – can indeed change shape over time. However, what changes is the input materials, defined as smart materials.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
